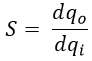Factors that Influence the Choice of a Transducer :
Some of the factors to be taken into consideration in the selection of transducer for a particular application are,
Operating Principle :
The first important factor for selecting a transducer is the operating principle. There are various transducers that use different operating principles like resistive, capacitive, piezoelectric, inductive, optoelectronic principle, etc.
Operating Range :
The operating range is also one of the important factors to be considered because every instrument has its operating rating for satisfactory operation. The input applied must lie within this operating range, so that the transducer can function with good resolution without any breakdown. The operating range of a transducer can be determined with its capabilities and error in the measurement.
Accuracy :
It is one of the most desirable characteristics of any transducer. The accuracy of a transducer is the degree of closeness of the output obtained to the true or ideal value. A transducer with high sensitivity can produce errors easily to other stimuli. The errors can be reduced using in-place system calibration and monitoring so that corrections are made accordingly to have a high degree of accuracy and repeatability.
Sensitivity :
It is also a desirable selection factor of a transducer. Every transducer should be sufficiently sensitive to the input applied to produce an output. The sensitivity of a transducer is the output obtained per unit change in the input quantity. Also, the sensitivity should not be either very high or low that leads to errors.
Stability and Reliability :
A transducer should have high stability and reliability. It should be stable to the external disturbances during its operation without deviating the output. The stability of the transducer also describes storage life.
Usage and Ruggedness :
A transducer should be mechanically rugged depending upon the application where it is used.
Transient Response and Frequency Response :
The transducer should have required time domain specifications such as settling time, rise time, peak overshoot and small dynamic error, etc.
Loading Effects :
The loading effect should be as minimum as possible so that errors in the measurement will be low. A transducer should have high input impedance and low output impedance for minimum loading effect.
Electrical Parameters :
The requirement for the type and length of cable signal to noise ratio when the transducer is used with amplifiers and the drawbacks of frequency response should also be considered.
Static Characteristics :
The selected transducer should have low hysteresis, high linearity, and high resolution.
Environmental Compatibility :
The factors of selection also include the consideration of environmental conditions. An incorrect choice of the transducer at a location to be operated where it can be subjected to temperature variation, vibration, and electromagnetic interference can affect the output.
After considering the above factors before selecting a transducer, it is important to know the characteristics of that transducer. The various characteristics of the transducer are,
Input Characteristics of Transducer :
The input characteristics of a transducer are as follows,- Type of input
- operating range/input range
- Loading effect.
Type of Input :
There are several transducers for measuring the various physical quantities. Specific transducers are designed to measure specific physical quantities. For example, a pressure transducer measures pressure, a temperature transducer measures temperature. Hence, a transducer is selected based on the type of input to be measured.
Input Range or Operating Range :
The operating range of a transducer is the range of values of input physical quantity that a transducer can accept and measure. While selecting a transducer for a certain application the operating range of that transducer for the respective input is also considered as a selection factor.
For example, a manometer can measure the pressures in the range of 10 to 106 pascals, an ionization gauge has an operating range of 10-12 to 10-3 Torr. The lower and upper limits of the operating range of a transducer can be determined from the transducer error and transducer capabilities.
Loading Effect :
When a transducer is employed to measure a certain quantity, the transducer may draw some of the energy or force or power from the quantity to be measured in order to carry out its operation (i.e., measurement process). This leads to inaccurate measurement of the quantity. Such a phenomenon is known as the loading effect. Hence, in order to ensure accurate measurements, a transducer should be free of the loading effect.
Transfer Characteristics of Transducer :
The transfer characteristics of a transducer need the attention of the following,
Transfer Function :
It is defined as the ratio of output quantity of a transducer to input quantity of that transducer and is given by,
Where, qo is the output of the transducer and qi is the input of the transducer. The Sensitivity is given by,
Generally, the sensitivity is not constant and depends on qi. But, in some cases, a linear relation exists between qo and qi. In those cases, the sensitivity will be constant throughout the range of the transducer. The inverse of sensitivity is known as the scale factor (i.e., dqi/dqo).
Error :
Errors occur when the relation qo = f(qi) is not followed by the transducer. Any variations in this expected function lead to errors. For a given qi, if qo' is obtained as output instead of qo then the error is given as,
- Scale error,
- Zero error
- Sensitivity error
- Hysteresis
- Nonconformity.
- Dynamic error
- Errors due to noise and drift
- Error due to variations in frequency.
- Zero error
- Sensitivity error
- Hysteresis
- Nonconformity.
Transducer Response :
The transducer response to the changes in environmental conditions should be given more attention while selecting a transducer for a particular application, otherwise expected and accurate results cannot be obtained.
Hence, the performance of a selected transducer should be completely defined by its transfer function and errors if it is in constant environmental conditions and not subjected to noise and disturbances such as variations in temperature, pressure, humidity, supply voltage, stray electromagnetic, and electrostatic fields, etc.
In any case, if the transducer is placed in these environmental disturbances, precautions should be taken to avoid the changes in transfer function and errors. One of the precautions is to provide guarding to the transducers.
Output Characteristics of Transducer :
The output characteristics of a transducer are,- Type of electrical output
- Output range
- Output impedance
Type of Electrical Output :
The type of electrical output of a transducer is also an important characteristic of a transducer because it may be used as an input to other stages of the system. The various electrical outputs of the transducer could be current, voltage, impedance, etc. A transducer output may not be applied directly as an input to the next stage.
In order to make a transducer output compatible with the subsequent stages, a signal conditioning circuit is used which may either convert its output from one form to another (for example, voltage to current) or change the amplitude of its output. Thus, depending upon the type of output, an appropriate signal conditioning circuit is selected.
Output Range :
Most of the transducers have a low-level output signal and so the output range will consist of low values. These low-level signals may not be able to drive other systems. Apart from it, the low-level signals may be affected by noise, due to which the lower limit of the useful output range is shifted to upper values, and hence the useful range is decreased.
The maximum input level is determined from the upper limit of the transducer's output range. By incorporating an amplifier in the output section inside a transducer, its output level can be increased as well as the output range can be increased.
Output Impedance :
When a transducer is connected to the next stage of the system, the next stage is prevented from loading effect if the output impedance of the transducer is zero. But, practically it is not possible to obtain completely zero output impedance. The loading effect can be reduced if the output impedance is very low.
A transducer acts as a constant voltage source if its output is a voltage signal and if its output impedance is lower than the input impedance of the next stage. A transducer has the characteristics of a constant current source if its output is current and if its output impedance is higher than the input impedance of the next stage. Whereas, if its output impedance matches the input impedance of the next stage (load impedance) then maximum power transfer takes place from the transducer to the next stage.